What is Chassis Wiring Vs Power Transmission
When it comes to wiring your car, there are two main types: power transmission wiring and chassis wiring.
Both types of wiring are essential, but they serve different purposes. If you don’t know the difference between the two, you could end up doing severe damage to your car.
Below, we’ll discuss the differences between power transmission wiring and chassis wiring and offer tips for choosing the right one for your needs.
Power Transmission Wiring.
Power transmission wiring carries electrical signals from the engine to the components that need them. This type of wiring is typically made from copper or aluminum and insulated to protect against short circuits and voltage spikes. In addition, power transmission wiring generally is bundled together in the loom, which makes it easy to route through the engine bay.
Chassis Wiring.
On the other hand, chassis wiring is used to carry electrical signals from components mounted on the vehicle’s chassis (such as headlights, taillights, and turn signals) to the main fuse box. This type of wiring is also typically made from copper or aluminum, but it is not insulated in the same way as power transmission wiring. Chassis wiring is generally routed through holes in the body of the vehicle, which makes it more susceptible to damage from water and other elements.
When choosing a type of wire for your project, it’s essential to remember its intended purpose. For example, a power transmission wire is designed to carry electrical signals from the engine to various components, while a chassis wire is intended to carry electrical signals from components mounted on the chassis to the main fuse box.
Keep these differences in mind when selecting wire for your project to ensure that you choose the right type for your needs.
Transmission Wiring Needs Thicker Gauge Wires
A car’s chassis wiring consists of all the wires that are separately routed, while the power transmission wiring holds wires that are tied in a bundle. The reason for this is that the power transmission wires need to be able to handle higher levels of current than the chassis wires.
The power transmission wires are also subject to more vibration than the chassis wires, so they must be better shielded against electromagnetic interference. Finally, the power transmission wires are more likely to short-circuit than the chassis wires, so they must be made from thicker gauge wire. These factors make the power transmission wiring system more expensive than the chassis wiring system.
PC Building Simulator Uncorrectable Hardware Error – User Guide
rlc talk
Amperage Capacity, Length, And Resistance Difference.
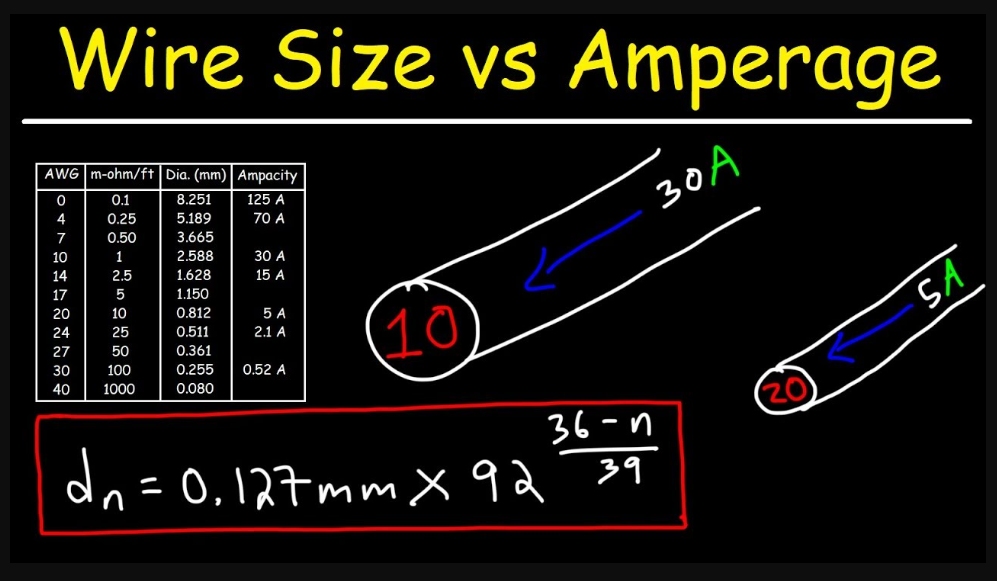
Chassis wiring and power transmission are two types of automotive wiring. They differ in amperage capacity, length, and resistance. Chassis wiring carries low-voltage signals and is used for accessories such as lights and horns. Power transmission wiring has high-voltage signals and is used for starting the engine and charging the battery.
Chassis wiring is typically made from copper or aluminum, while power transmission wiring is generally made from steel. Chassis wiring is typically shorter and has a lower resistance than power transmission wiring. Power transmission wiring generally is longer and has a higher resistance than chassis wiring. Chassis wiring is typically less expensive than power transmission wiring. Chassis wiring is more likely to be replaced than power transmission wiring.
Power Transmission Has Some Overheating Problems
Power transmission wiring is usually made up of multiple conductor wires that are bundled together. The conductor wires are typically made from copper or aluminum and are insulated with a dielectric material.
The dielectric material helps to prevent the conductor wires from touching each other, which could cause a short circuit. Power transmission wiring is typically positioned in a bundle, which helps to keep the conductor wires from coming into contact with each other.
However, this also means that the power transmission wiring faces low air conduction. As a result, the power transmission wiring can often become overheated, leading to problems such as voltage drop and loss of electrical power.
Power Transmission Work Slow
Power transmission wiring is an essential part of the electrical grid. However, it can sometimes work slowly due to a lack of aeration. This is because all the wires are routed together, which can prevent air from circulating correctly.
As a result, the wiring may overheat and become damaged. To prevent this, it is essential to aerate the power transmission wiring by routing the wires separately. This will allow air to circulate more freely and will help to keep the wiring cool and functioning properly.
Different use cases
Chassis wiring in a vehicle provides power to the engine, lamps, and other devices. The wire used is typically a stranded copper conductor with insulation of PVC or another suitable dielectric. Depending on the application, the wire may be bare or tinned. The current rating for chassis wiring is usually 15 to 20 amps.
On the other hand, power transmission wiring is used to connect the battery to the starter and alternator. The wire used for this application is usually a stranded copper conductor with insulation of PVC or other suitable dielectrics.
The current rating for power transmission wiring is usually 30 to 40 amps. Both types of wiring are available in various gauges (AWG) to suit the application. Chassis wiring is typically 18 AWG, while power transmission wiring is usually 16 or 14 AWG. Chassis wiring is also available in shielded and unshielded versions.
Shielded versions have a metallic braid that helps to reduce interference from external sources. Unshielded versions do not have this braid and are typically used for applications where interference is not a concern.
Power transmission wiring is also available in shielded and unshielded versions. Shielded versions have a metallic braid that helps to reduce interference from external sources. Unshielded versions do not have this braid and are typically used for applications where interference is not a concern.
Eagle vs Altium Designer PCB Software; Best Comparison.
Rlc talk